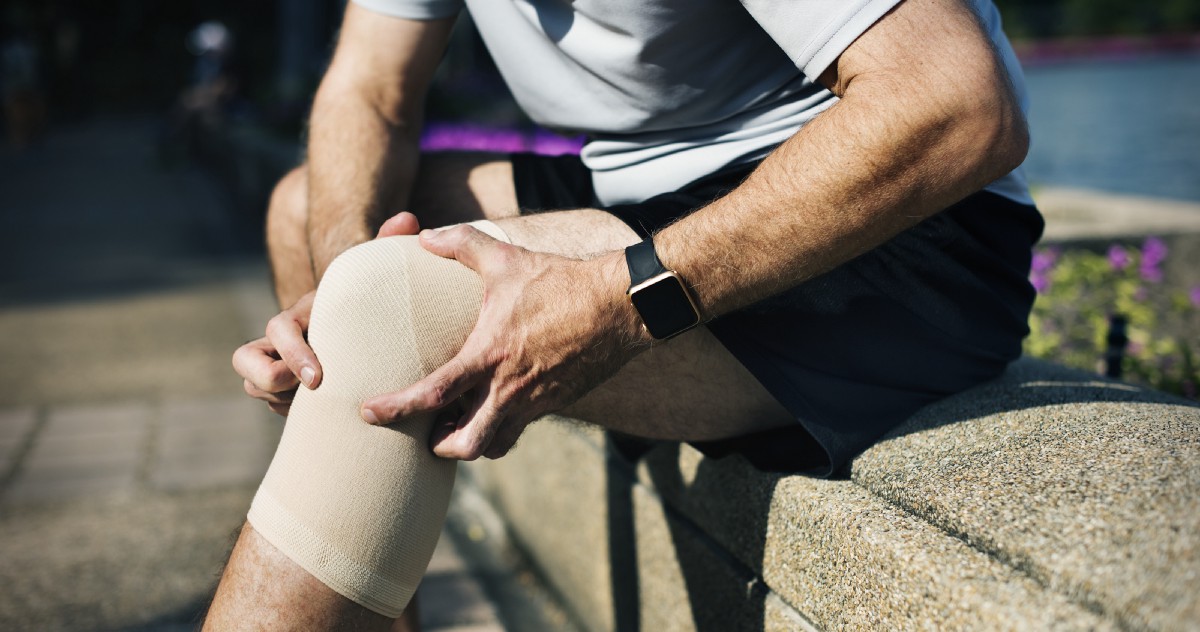
If you are among the many people plagued by muscle cramps or “charlie horses” as they are called, you should find this article from Markham Heid interesting. It was published in Medium, August 9th 2018.
Here’s a Summary
Muscle cramps are a common condition that affect 30% of adults in the United States. The commonly accepted theory for what causes them includes fluid imbalances; dehydration and not enough electrolytes. However, recent evidence seems to suggest there’s more to it.
Evidence that it may Not be Low Electrolytes
Researchers at Goethe University conducted research on marathon runners to see who experienced muscle cramps. What they found is that runners struck by cramps had the same levels of electrolytes as runners that weren’t. This likely means that electrolytes are only a possible contributor to cramps in certain situations, rather than a blanket cause. The theory is even further strengthened when considering research that shows ingesting more electrolytes doesn’t help stop cramping. When it comes to actually curing cramps, the researchers suggest thinking of cramps as a disorder in our nerves instead of the muscle itself.
Humans have something called the Golgi tendon organ, a part of the nervous system that exists at the intersection of muscles and tendons. Basically, it regulates how hard your muscles contract. If something interferes with it, your muscles can contract to the point where they cause pain. This idea starts to make even more sense when you consider that cramps are commonly associated with conditions that cause nerve damage: ALS, Type 2 Diabetes, and aging.
What To Do About Muscle Cramps
Unfortunately, it seems like most advice for stopping muscle cramps isn’t very effective. The piece of advice that seems to hold the most weight is that stretching out your muscles while a cramp is beginning helps prevent it. However, preventative stretching before bed was shown not to decrease night cramps. Also, while fluid to electrolyte imbalances aren’t the end all cause of cramps, maintaining a good balance is still good for you, and can possibly increase your cramp resistance.
While not having an easy cure might be disheartening, there is are several cramp treatments still in testing that look promising. Electrical stimulation of muscle was shown to reduce cramping in both healthy individuals and individuals with increased inclination for cramps. Several drugs are also being developed that try to regulate our body’s electrical activity and muscle excitability. It won’t be long until muscle cramps are a thing of the past.
Read more about muscle cramps at the original article published on Medium.
To learn about the importance of hydration aside from electrolytes and cramps, check out this other article from us: Drink Enough Water? Even 1% Dehydration Could Be Slowing Your Mental Processes

 Scan Me!
Scan Me!